Tubal Reversal
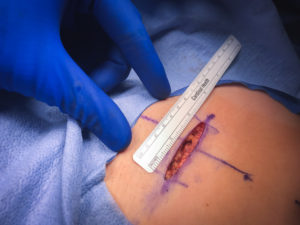
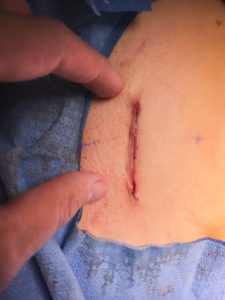
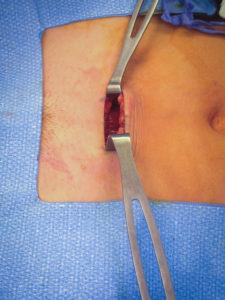
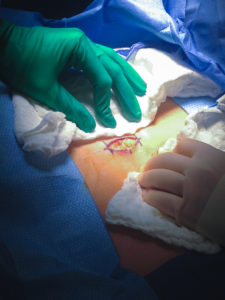
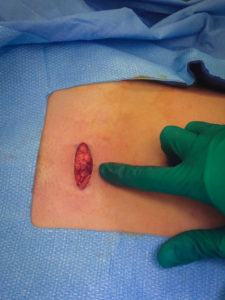
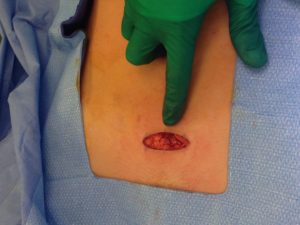
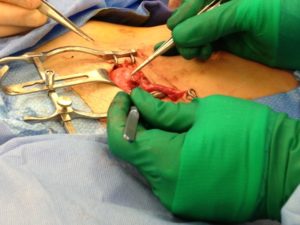
Our tubal reversal (TR) surgery is accomplished using a minimally invasive technique. Patients typically have a 2-3 inch incision at the top of the pubic hairline (bikini incision) and are able to go home the SAME DAY of the surgery. The surgery takes 1-2 hours to complete. The patient will need someone to drive them to and from the surgery. If you live out of town, you should consider staying overnight in a nearby hotel.
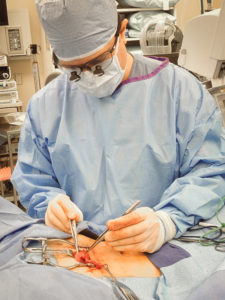
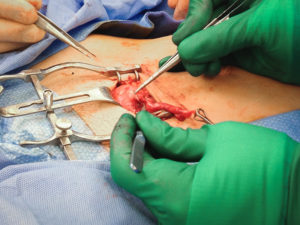
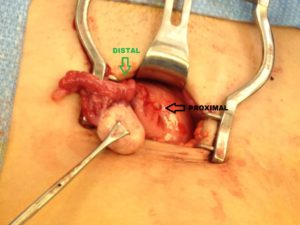
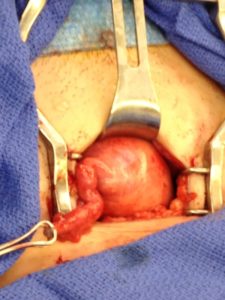
Tubal ligation reversal utilizes microsurgical techniques to open and reconnect the fallopian tube segments that remain after a tubal ligation procedure. In most cases there are two remaining segments, the proximal tubal segment that emerges from the uterus, and the distal tubal segment that ends with the fimbria. The scar tissue that exists between the two segments of the fallopian tube is first removed. Very fine suture is then used to reconnect the segments and allow the reestablishment of a pathway for a future embryo to travel. Patency of the tubes is confirmed by injecting blue dye through a catheter that has been placed inside the uterine cavity. For more complicated cases (history of multiple abdominal surgeries such as C-sections, history of PID (pelvic inflammatory disease), chlamydia or gonorrhea infection, history of pelvic pain or endometriosis), or when we have no evidence of how much damage to the tubes was done during the ligation, the patient may benefit from having a laparoscopy done first to diagnose and possibly remove scar tissue prior to the start of the Tubal Reversal. A laparoscopy requires a 1cm navel incision to place a small camera into the abdominal cavity. This allows us to assess tubal length and overall anatomy before proceeding with the mini-laparotomy incision for the Tubal Reversal. We have negotiated with the surgery centers we use to get a reduced cash pay price for the laparoscopy.
SUCCESS RATES
The procedure is highly successful, with average pregnancy rates in the 60-70% range, being even higher in younger patients and lower in an older population. The success of the procedure is based on the couple’s fertility potential, the type of ligation performed (clip, ring, cutting, tying, burning, removal of the tube), and the amount of tube left and the health of the fimbria.
Expected pregnancy rates by age and method of tubal occlusion:
| Age (years) | Pregnancy Rate (%) | Clip/Ring (%) | Ligation/burning/resection (%) |
|---|---|---|---|
| >30 | 80s | 80-90 | 75-80 |
| 30-34 | 70s | 75-80 | 70-75 |
| 35-39 | 60s | 65-70 | 60-75 |
| >39 | 30s | 30-35 | 25-30 |
Most of the tubal ligations can be reversed, but in a small percentage of patients only one tube can be fixed; rarely both sides are inoperable. If only one tube is patent after surgery, the pregnancy rates stay about the same, but the time to accomplish pregnancy may be twice as long.

POST OP
To help manage pain in the post-operative period, the patient will use Lidoderm strips placed above and below the incision to help decrease the amount of narcotics she will need. Most patients can transition to Ibuprofen for pain control after the initial few days. The patient can return to work in about 2 weeks. At the 2 week post-operative visit, we will review the surgical findings and outcome and inspect the incision for any signs of infection.
CONCEIVING AFTER THE SURGERY
You may attempt pregnancy the cycle AFTER the procedure. Most people conceive in 6 months. For women that have a 28-30 day menstrual cycle, the day of ovulation is around cycle day 14. Ovulation predictor kits (OPKs) may be purchased over-the-counter and used to improve the timing of intercourse. If not using OPKs then you can start having intercourse around cycle day 11 and continue every other day until cycle day 17.
To reduce the complications from the increased risk of ectopic pregnancy, we ask our patients to strictly follow our guidelines of performing a urine pregnancy test after missed menses. If your home pregnancy test is positive, then you will need close follow up with us or your OB doctor. Blood pregnancy testing is more accurate than urine and these levels should be followed carefully. An early ultrasound (around 5.5 weeks) is recommended to confirm location of the pregnancy. Even if a tubal pregnancy is identified, patients who adhere to this monitoring are usually successfully treated medically, thus avoiding further testing, risks and surgery.
If you are over 35 years old (or if you have low ovarian reserve) and have not conceived in the first 6 months, then we recommend evaluation of the tubal patency with the hysterosalpingogram (outpatient radiology procedure). If you are less than 35 years old (and have good ovarian reserve) you can attempt pregnancy for one year before being reevaluated.

REQUEST AN APPOINTMENT
Schedule your consultation today!